What is a Safe Care Environment?
A safe care environment refers to a healthcare setting where patients, staff, and visitors are protected from potential harm, ensuring the well-being of all individuals involved. It encompasses various aspects of safety, including physical, psychological, and cultural dimensions. In the context of healthcare organisations and in alignment with standards like NSQHS (National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards), Aged Care Quality Standards, and Strengthened Aged Care Standards, a safe care environment entails the following key elements:
- Physical Safety: This aspect focuses on minimising physical risks and hazards within the healthcare facility. It involves measures to prevent accidents, injuries, and the spread of infections.
- Psychological Safety: Psychological safety is equally important in healthcare. It involves creating an environment where patients, staff, and visitors feel respected, valued, heard, and supported.
- Cultural Safety: Cultural safety acknowledges the diverse backgrounds of patients, staff, and the broader community served by healthcare organisations. It promotes inclusivity, understanding, and respect for different cultural values, beliefs, and practices.
What is the Safe Care Environment Training Requirement?
Training requirements for a safe care environment are rigorous, given the critical nature of healthcare. To meet the standards set by NSQHS and Aged Care Quality Standards, your training program must include education and support to meet the following requirements/action.
Relevant Standards
The health service ensures safety and care quality:
- Through the actual design of the care environment and organisation
- By maintaining infrastructure, devices, equipment and other factors fit for purpose
Action 1.30: Service environment reviews
The environment is reviewed to:
- Identify areas of high risk unpredictable behaviours
- Create strategies to minimise the risks for patients, cares, families and the workforce
- Develop access to quiet and calm care environment where clinically necessary
Action 1.31: Clear signage and directions
- The health organisation supports access to services and facilities via clear signage to services and facilities
Action 1.32: Overnight admissions
- Processes in place to allow flexible visiting arrangement that facilitates safety, and meets the patient's needs
Action 1.32: Cultural considerations
- A welcoming environment that recognises cultural beliefs and practices of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 5.3 (b): The service environment:
- (i) Is clean, safe, comfortable and well maintained
- (ii) Facilitates free movement in indoor and outdoor settings
Action 4.1a.1: Home environment
Providers ensure the home environment is safe by:
- Identifying risks to client safety
- Discussing said risks with the client
Action 4.1a.2: Equipment and aid safety
Providers ensure the home environment is safe by:
- Ensuring safe, clean, and well-maintained equipment and aids
Action 4.1a.2: Service environment (part 1)
Providers implements an environment that:
- Is safe, welcoming and comfortable
- Is well-maintained and routinely cleaned
- Is fit for purpose
Action 4.1b.1: Service environment (part 2)
Providers implements an environment that:
- Reduces safety risks (without mitigating movement), optimises useful stimulation and is easy to navigate
Action 4.1b.2: Service environment (part 2)
The provider ensures the service environment:
- a. is accessible, including for older people with disability
- b. promotes movement, engagement and inclusion through design
- d. unobtrusively reduces safety risks, optimises useful stimulation and is easy to navigate.
Action 4.1b.3: Service equipment safety
Equipment used in the delivery of care and services is safe, clean, well- maintained and meets the needs of older people.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the antimicrobial stewardship training requirement:
Skills Required by Staff to Reinforce Safe Care Environments
Staff members must possess a range of skills to reinforce safe environments effectively.
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Environmental Safety | This includes skills related to maintaining a safe and clean physical environment within the healthcare facility. Staff should be knowledgeable about proper sanitation, maintenance, and the identification and mitigation of environmental hazards. |
| Communication Skills | Staff should be trained in active listening, clear and empathetic communication with patients and colleagues, and conflict resolution. |
| Emergency Response Skills | Staff must be trained to remain calm and respond swiftly to critical situations such as cardiac arrests, fires, or natural disasters. Regular drills and simulations are essential for skill development. |
| Cultural Sensitivity | Staff should receive training on cultural competency, addressing cultural biases, and ensuring equitable care for all patients, regardless of their backgrounds. |
| Infection Control Skills | Training should cover proper hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment, and the handling and disposal of hazardous materials. Staff should be aware of infection control policies and procedures. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Safe Care Environments
Assessing staff competency is a critical step in ensuring a safe healthcare environment. To do so effectively:
- Conduct Regular Competency Assessments: Implement a structured assessment schedule, including initial assessments for new hires and ongoing assessments for existing staff.
- Utilise Multiple Assessment Methods: Assessments should involve a combination of methods, including observation, simulations, written tests, and peer evaluations. This multifaceted approach provides a comprehensive view of staff competence.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: After assessments, offer feedback that highlights strengths and areas for improvement. Create personalised development plans to address any identified deficiencies.
- Document and Monitor Progress: Maintain detailed records of assessment results and progress over time. This documentation helps in tracking individual development and overall program effectiveness.
By regularly assessing staff competence, you can identify areas for improvement and tailor training accordingly.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Reinforce Safe Care Environments Skills
Supporting employees in developing skills to reinforce safe environments is vital. Consider these strategies:
- Offer Regular Training Sessions and Workshops: Create a calendar of training sessions and workshops that cover various aspects of safe care environments. Ensure that these sessions are accessible to all staff members.
- Provide Access to Online Resources and E-Learning Modules: Develop an online platform with resources, e-learning modules, and reference materials. This allows staff to access training materials at their convenience and facilitates continuous learning.
- Encourage Mentorship and Peer Learning: Foster a culture of mentorship, where experienced staff members guide newer employees. Peer learning can be an effective way to share best practices and experiences.
- Reward and Recognise Excellence: Acknowledge and reward staff who excel in maintaining safety standards. Recognitions can include certificates, awards, or promotions, creating a sense of accomplishment and motivation for others.
Sample Training Plan for the Safe Care Environment Training Requirement
Safe care environment knowledge and skills can be reinforced and strengthened with an effective training plan based on your organisation's specific requirements.
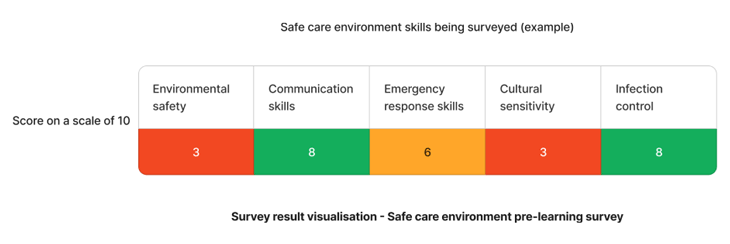
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skills that requires the most attention are environmental safety skills and cultural sensitivity skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Clinical skills | |
| Q2 | Clinical skills |
Need an LMS that can support safe care environment training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your safe care environment requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Safe Care Environments - Example
To assess your healthcare staffs competence in safe care environments, consider asking these four survey questions:
Staff Survey - Safe Care Environment Competency
-
How would you respond to a patient's complaint about privacy?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you promote cultural sensitivity and diversity in your interactions?
- [Answer here]
-
How would you handle a situation where a patient or colleague raises concerns about the safety of the care environment?
- [Answer here]
-
Have you received training on our organisation's safety policies?
- 1. Yes
- 2. Somewhat
- 3. No
Conclusion
Developing a training program for safe healthcare environments is paramount in ensuring the well-being of patients and staff. By focusing on physical, psychological, and cultural safety, equipping staff with essential skills, assessing competency, and implementing supportive strategies, healthcare organisations can create a culture of safety and excellence in patient care.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Clinical Governance Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.29'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.30'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.31'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.32'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.33'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. Aged Care Quality Standards, ' Standard 5. Organisation's service environment - Requirement 5.3.(b)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 4.1a.1-4.1b.3'



