Supporting Staff Through L&D Best-Practice
Robust learning and development strategies are essential in the highly regulated health and aged care sector. This is because we need staff to possess specific skills and capabilities to perform their duties to the highest standard. Competency mapping is an L&D best practice that is essential for supporting staff in performing their roles effectively. This comprehensive guide explores the concept of competency mapping, its specific application, and the significant role learning analytics plays in enhancing this process.
What is Competency Mapping?
Competency mapping is a strategic approach used in learning and development to systematically identify, document, and analyse the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviours required for effective performance in a job role.
This process is vital for aligning employee performance with an organisation's strategic goals and training and education programs. It provides a structured framework for assessing and developing employee capabilities. It ensures that training management is closely aligned with the workplace's actual needs, enhancing the overall quality of learning experiences and effectiveness of the investment.
Why is Competency Mapping Important?
Competency mapping involves defining competencies for the entire interprofessional team, which includes numerous roles, capabilities, and skill levels, such as registered health professionals, administrative staff, and care and support workers.
A comprehensive approach to identifying the required skills, knowledge, and behaviours necessary for the different roles allows staff to undertake more targeted training and education opportunities relevant to the person's organisational and career development needs. By focusing on defined competencies, organisations can prepare their staff to meet the unique challenges of the clinical environment, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes and efficiency in care services.
What’s Involved in Competency Mapping?
Competency mapping involves several key steps. First, it requires identifying the core skills, knowledge, and behaviours necessary for a role. These can include technical competencies, such as proficiency in specific clinical or non-clinical skills or digital information systems, and behavioural competencies, like communication skills and teamwork. Next, these competencies are defined at varying levels—basic, intermediate, or advanced—to reflect different degrees of expertise and proficiency.
After defining the competencies, they are mapped to specific roles or job functions within the organisation, helping to clarify the expectations for employees in those positions. The next step is assessing employees to determine their current competency levels and identifying any gaps that may need to be addressed through targeted training or development.
Finally, competency mapping ensures that the identified competencies align with the organisation’s strategic objectives, enabling employees to contribute effectively to the organisation’s overall success.
Using Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping
Learning analytics involves collecting, analysing, and reporting data about learners and their learning experiences. In competency mapping, these analytics are instrumental in identifying skills gaps, monitoring the learning process, enhancing student engagement, and developing a prediction model to tailor educational content to individual needs. Leveraging data about learners allows healthcare educators to create a dynamic, responsive learning environment that adapts to the changing needs of healthcare professionals.
What's the Difference Between a Competency and a Capability?
Competencies refer to the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviours an individual needs to perform a particular job effectively. At the same time, capabilities are broader, encompassing the overall ability to achieve outcomes by applying a range of competencies. Competencies are focused on individual tasks and are easier to measure, whereas capabilities involve the capacity to respond to various challenges and are more holistic, combining multiple competencies and resources. In essence, competencies are the building blocks that contribute to broader capabilities (Acorn, 2024).
Using Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping
Learning analytics involves collecting, analysing, and reporting data about learners and their learning experiences. In competency mapping, these analytics are instrumental in identifying skills gaps, monitoring the learning process, enhancing staff engagement with the learning and development process, and developing a prediction model to tailor educational content to individual needs. Leveraging data about learners allows educators and L&D teams to create a tailored learning program for the varied staff in the interprofessional environment.
Steps to Perform Competency Mapping with Learning Analytics
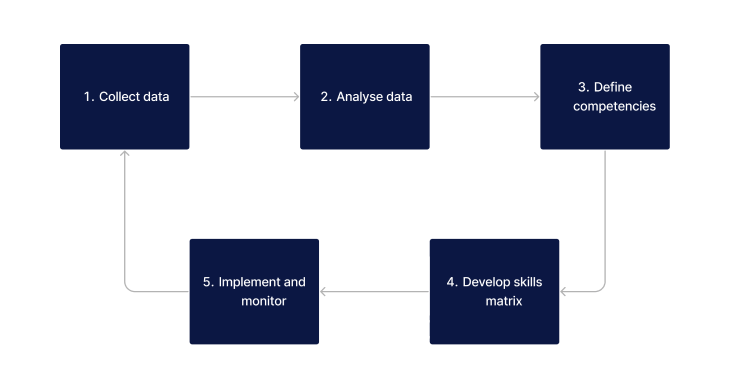
To effectively use learning analytics in competency mapping, several critical steps must be followed:
- Data Collection: Begin with comprehensive data collection about learners’ performance, engagement, and feedback from various sources like learning management systems and staff feedback from learning.
- Analyse Data: Reflect and assess this data, focusing on identifying skills gaps, evaluating the effectiveness of current training modules, and understanding learners' preferences and challenges.
- Define Competencies: Based on the analysis, define the specific competencies required for different roles, ensuring they align with the overall goal of providing quality care.
- Develop a Skill Matrix: Create a comprehensive skill matrix that aligns the identified competencies with healthcare roles and responsibilities. This matrix acts as a roadmap for training plans, education, skill development, and career progression.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the competency map in training programs, continuously monitoring its effectiveness and making data-driven adjustments to keep it relevant and effective.
Tips for Using Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping
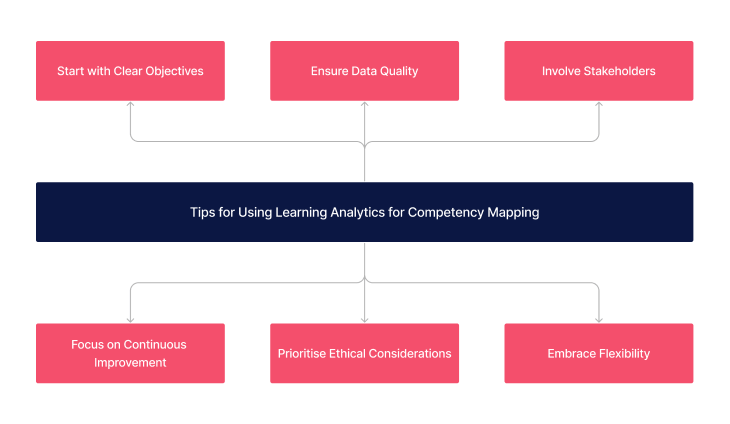
Implementing learning analytics in competency mapping can be complex but rewarding. Here are some tips to make the most of this approach:
- Start with Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve with analytics in competency mapping. Having clear goals helps in guiding the data collection and analysis process.
- Ensure Data Quality: The insights drawn from analytics are only as good as the data collected. Ensure accuracy and relevance of data for meaningful outcomes.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage other educators, people in the L&D team, staff (learners), and other teams, such as the Quality department, in the process to ensure the competency map reflects the real-world requirements and challenges of staff and the organisation.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Use analytics as a tool for ongoing evaluation and refinement of training programs, adapting to new trends and learner feedback.
- Prioritise Ethical Considerations: Always consider the privacy and security of learner data. Adhere to ethical guidelines and legal requirements in data handling and analysis.
- Embrace Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust your strategies based on the insights gained from analytics. Flexibility is key in responding to evolving learning needs and industry demands.
Tools for Competency Mapping with Learning Analytics
To effectively implement competency mapping with learning analytics, various tools and technologies can be utilised:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): The Ausmed LMS, as well as Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas offer robust analytics features, track learner progress and engagement.
- Data Visualisation Tools: Tools like Tableau and Power BI help in presenting complex data in an understandable format, aiding in decision-making.
- Online Assessment Platforms: Platforms such as ProProfs Quiz Maker and SurveyMonkey provide valuable data on learner knowledge and skills.
- Feedback and Survey Tools: Tools like Google Forms and Qualtrics are essential for collecting learner feedback, an important aspect of the analytics process.
- Custom Analytics Solutions: Tailored solutions developed specifically for your organisation can provide more targeted insights aligned with specific competency needs.
Conclusion
Both staff and organisations aim to perform their roles consistently and effectively. Creating scalable methods to support staff in achieving organisational goals and personal career objectives is essential for employee satisfaction and retention. By enabling staff to learn, grow, and develop specific skills that align with the organisation’s needs for their particular job roles, organisations can build capacity and enhance staff success. Competency mapping, supported by clear learning data, helps L&D teams achieve these outcomes.
Want a healthcare LMS that supports competency mapping using learning analytics?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Related Resources
- Guide to Mandatory Training
- LMS in Healthcare: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- What Are Learning Analytics?
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Collection for Learning Analytics
- What Are the Key Learning Analytics Metrics?
- How to Create a Culture of Continuous Learning
- Guide to Compliance Training (for Healthcare Managers)
- Guide to Building a Competency Framework for Skill Development
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- A Guide to Personalised Learning in Healthcare
References
- Carney, P. A., Sebok-Syer, S. S., Pusic, M. V., Gillespie, C. C., Westervelt, M., & Goldhamer, M. E. J. (2023). Using learning analytics in clinical competency committees: Increasing the impact of competency-based medical education. Med Educ Online, 28(1), 2178913. https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2023.2178913.
- Thoma, B., Ellaway, R. H., & Chan, T. M. (2021). From Utopia Through Dystopia: Charting a Course for Learning Analytics in Competency-Based Medical Education. Academic Medicine, 96(7S), S89-S95. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000004092.
- Bojic, I., Mammadova, M., Ang, C. S., Teo, W. L., Diordieva, C., Pienkowska, A., Gašević, D., & Car, J. (2023). Empowering Health Care Education Through Learning Analytics: In-depth Scoping Review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 25, e41671. https://doi.org/10.2196/41671.
- Acorn. (2024). Competency vs. Capability: What’s the Difference? Acorn Works. https://acorn



