What are Standard Precautions?
Standard precautions represent the primary strategy for minimising the risk of transmission of infectious agents. They include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), safe handling of potentially contaminated equipment or surfaces, and respiratory hygiene. These precautions are based on the principle that all blood, bodily fluids, secretions and mucous membranes may contain transmissible infectious properties.
What are Transmission-Based Precautions?
Transmission-Based Precautions are additional infection control measures applied for patients known or suspected to be infected with pathogens that can be transmitted by airborne, droplet, or contact routes. These precautions are used in conjunction with Standard Precautions and are tailored to the specific mode of transmission by the pathogen.
Importance of Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions
Implementing standard and transmission-based precautions is vital for protecting healthcare workers, patients, and visitors from the spread of infectious diseases. These precautions help prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), enhance patient safety, and are fundamental to infection control programs in healthcare facilities.
What is the "Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions" Training Requirement?
Healthcare organisations must ensure that all staff are trained in standard and transmission-based precautions as part of their workplace orientation and receive ongoing education to maintain their competency. The NSQHS and ACQS mandate this training to improve the quality of care and patient safety.
Relevant Standards
Processes for applying the standard and transmission-based precautions are aligned to the Australian Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare, as well as jurisdictional laws, requirements, and policies.
The health service has:
- Collaborative and consultative processes for the assessment and communication of infection risks to patients and the workforce
- Infection prevention and control systems, are in conjunction with the hierarchy of controls, in place to reduce transmission of infections.
- Processes for the use, training, testing and fitting of personal protective equipment by the workforce
- Processes to monitor and respond to changes in scientific and technical knowledge about infections, relevant national or jurisdictional guidance, policy and legislation
- Processes to audit compliance with standard and transmission-based precautions
- Processes to assess the competence of the workforce in the appropriate use of standard and transmission-based precautions
- Processes to improve compliance with standard and transmission-based precautions
The healthcare workforce apply standard precaution and transmission-based precautions when required, and consider:
- The process of assessing the risks to patients starts at the point of referral, continues upon their admission or initial presentation for care, and is consistently revisited throughout their care
- The assessment includes determining if a patient is affected by any communicable diseases, or has a current or past colonisation or infection with significant organisms, whether of local or broader national concern.
- Considerations for the placement and accommodation of patients are made to both prevent and control the risk of infections.
- Attention is given to the potential effects on the mental and physical health of patients who are placed in isolation.
- To minimise risks, environmental controls are implemented, which encompass, but are not limited to, the management of heating, ventilation, and water systems, alongside considerations for workflow, facility layout, and the choice of surface materials.
- Specific safety measures are undertaken when transporting patients either within the healthcare facility or to and from different external services.
- There may be a requirement for enhanced environmental cleaning or disinfection, necessitating additional resources and processes.
- The nature of the medical or surgical procedure being conducted is also a key consideration.
- The provision of equipment essential for the routine care of patients is carefully planned and managed.
Processes are in place to::
- Examine information regarding infections prevalent in the community to gauge their potential effects on patients and staff, and take appropriate action in response.
- Share information about a patient's infection status throughout their care, including when care is handed over from one provider to another.
- Offer essential details to patients, their families, and caregivers concerning their infection status, the associated risks of infection, and the specifics and expected duration of measures taken to prevent infection transmission.
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Action 3.1.2: Infection prevention system requirements
The provider implements a system for infection prevention and control that is used where care and services are delivered:
- identifies an appropriately qualified and trained infection prevention and control lead
- describes standard and transmission-based precautions appropriate for the setting, including cleaning practices, hand hygiene practices, respiratory hygiene, cough etiquette and waste management and disposal
- prioritises the rights, safety, health and well- being of older people
- complies with contemporary, evidence- based practice
- includes additional precautions to respond promptly to novel viruses and outbreaks of infectious diseases (suspected or confirmed)
- communicates and manages infection risks to older people, family, carers and workers
- is informed by worker and older person immunisation and infection rates.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the "standard and transmission-based precautions" training requirement:
What Skills Do Staff Need for Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions?
A comprehensive skill set is required for healthcare professionals to effectively support standard and transmission-based precautions. These skills not only ensure the safety of patients but also protect healthcare workers from potential infections.
- Correct use of personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes selecting appropriate PPE for different situations, using proper donning and doffing techniques, and understanding the limitations of each type of PPE.
- Hand hygiene techniques: Involves mastering the WHO's 'Five Moments for Hand Hygiene', understanding the differences between handwashing with soap and water and using alcohol-based hand rubs, and recognising the critical times hand hygiene should be performed.
- Waste management and disposal procedures: Covers waste segregation into clinical and non-clinical waste, safe handling practices to minimise exposure to sharps and other infectious materials, and understanding the regulations surrounding disposal.
- Environmental cleaning and disinfection practices: This entails knowing the correct use of cleaning agents and disinfectants, the frequency of cleaning various surfaces and equipment, and the importance of targeted cleaning in outbreak situations.
- Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette: This etiquette focuses on measures to minimise the risk of respiratory infections spreading, including the use of masks, covering coughs and sneezes, and maintaining spatial distance from others when symptomatic.
(Clinical Excellence Commission 2020)
How to Assess Staff in Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions
Regular assessment of staff competency in standard and transmission-based precautions is important to ensure the effectiveness of training programs and adherence to infection control practices.
| Skill | Assessment Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Hand hygiene | Observation of technique during routine care, feedback sessions, and quizzes to reinforce best practices. | Regularly conduct hand washing audits throughout the year. |
| Use of PPE | Practical demonstrations are assessed by a qualified observer, followed by constructive feedback and re-demonstration if necessary. | Bi-annually, or as protocols are updated or new PPE is introduced. |
| Environmental cleaning | Audit cleaning practices using checklists, direct observation, and swab tests to measure cleanliness. | Ensure this is done regularly, with periodic reviews in case of infection outbreaks. |
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Develop Skills in Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions
Developing and sustaining the skills necessary for effective infection control practices requires a strategic approach to training and development.
- Regular training sessions incorporating the latest guidelines: Ensure training content is up-to-date with the latest evidence-based practices and guidelines. Use a variety of training methods to suit different learning styles, including interactive workshops, online modules, and practical demonstrations.
- Simulation exercises to practice and refine skills: Create realistic scenarios that allow staff to practice their skills in a safe environment. Simulations can help identify areas for improvement and build confidence in handling real-life situations.
- Peer reviews: Encourage a culture of open feedback among peers to enhance learning and accountability. Peer review sessions can be structured to focus on specific skills, with participants providing constructive feedback based on observed practices.
- Access to resources and updates on infection control practices: Provide staff with easy access to guidelines, instructional videos, and other resources for reference and continuous learning. Regularly update these resources to reflect current best practices.
Sample Training Plan for the "Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions" Requirement
A structured training plan is vital for systematically enhancing standard and transmission-based precautions.
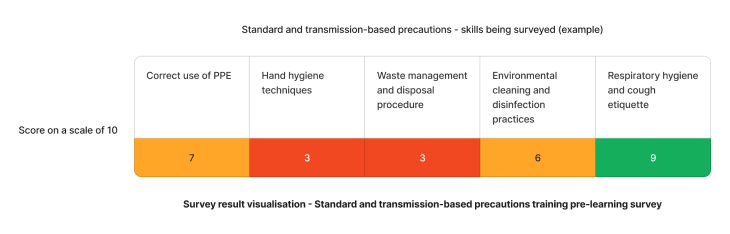
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example, the skills requiring the most attention for standard and transmission-based precautions in healthcare are hand hygiene techniques and waste management and disposal procedure skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Hand hygiene techniques | |
| Q2 | Waste management and disposal procedures |
Need an LMS that support can standard and transmission-based precautions?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions - Example
Consider the following survey questions to evaluate staff's communication skills for standard and transmission-based precautions:
Staff Survey - Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions Competency
-
How frequently should hand hygiene be performed before and after patient contact?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe the correct sequence for donning and doffing PPE.
- [Answer here]
-
What are the key differences between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilisation?
- [Answer here]
-
Identify situations where airborne precautions are necessary over standard precautions.
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Developing and implementing a comprehensive training program on standard and transmission-based precautions is vital for healthcare workers' and patients' safety and well-being. By focusing on the skills required, assessing staff competencies, and employing strategies for skill enhancement, healthcare organisations can significantly reduce the risk of infection transmission and improve overall care quality.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'Preventing and Controlling Infections Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'Australian Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.06'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.07'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.08'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.09'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 1.1.4, 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.2'
- Clinical Excellence Commission 2020, Personal Protective Equipment for Contact, Droplet and Airborne Precautions, online video, 7 April, viewed 28 August 2024, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tfITL694UAQ



