What are Restrictive Practices?
Restrictive practices are interventions that involve force, control, or restraint, which can limit an individual's rights or freedom of movement. These practices are sometimes necessary to ensure the individual's or others' safety; however, they must be used judiciously, ethically, and as a last resort. Inappropriate use can result in physical harm, psychological trauma, and violation of an individual's rights. The overarching aim within the healthcare sector, particularly in aged and disability care, is to minimise these practices as much as possible, employing them only when necessary and in the least restrictive form.
Types of Restrictive Practices
Understanding the different forms of restrictive practices is crucial for healthcare professionals. This knowledge ensures that staff can identify, prevent, and if needed, correctly apply the least restrictive option. Here are the most common types:
- Physical restraint: Using manual or mechanical means, such as belts or rails, to restrict a patient's voluntary movement.
- Chemical restraint: Medications are used not to treat a medical condition but to control behaviour.
- Environmental restraint: Structural or mechanical alterations that restrict free movement or access to one's own body.
- Seclusion: Isolation of an individual in a room or area from which free exit is prevented (Department of Health & Aged Care 2024).
What is the "Minimising Restrictive Practices" Training Requirement?
In line with Actions 5.35 and 5.36 of the NSQHS and Action 3.3(a) from the Aged Care Quality Standards, healthcare organisations are mandated to provide comprehensive training to minimise restrictive practices. This training is integral to ensure that staff are well-informed of the legalities, ethical considerations, and the various less-restrictive alternatives that could be used. The training should include an understanding of behaviours, the impact of these practices on individuals, and the importance of person-centred care, which respects the rights and choices of individuals.
Relevant Standards
Action 5.35: Minimising restrictive practices: restraint:
Where restraint is necessary (clinically), processes and systems are in place to:
- Minimise or eliminate (where possible) the use of restraint
- Manage the use of restraint to follow legislation
- Report any use of restraint to the governing body
Action 5.36: Minimising restrictive practices: restraint:
Where restraint is necessary (clinically), and is permitted under legislation, processes and systems are in place to:
- Minimise or eliminate (where possible) the use of seclusion
- Manage the use of seclusion to follow legislation
- Report any use of seclusion to the governing body
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 3.3 (a): High-impact or high-prevalence risks:
Each consumer gets safe and effective personal care, clinical care, or both personal care and clinical care, that:
- Is best practice
- Is tailoured to their needs
- Optimises their health and well-being
Action 3.2.7: Minimising the use of restrictive practices:
If used, these practices are:
- a) used as a final resort
- b) used in the least restrictive manner and for minimal time
- c) used with informed consent
- d) monitored and regularly reviewed
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the medication review training requirement:
What Skills Do Staff Need for Minimising Restrictive Practices?
To effectively minimise restrictive practices, healthcare staff require a diverse skill set, grounded in empathy, communication, and a thorough understanding of individualised care. These skills include:
- De-escalation techniques: The ability to diffuse potentially volatile situations calmly and safely.
- Person-centred care: Tailoring care approaches to respect the individual's preferences, needs, and values.
- Trauma-informed care: Recognising and understanding the prevalence and impact of trauma to avoid re-traumatisation.
- Legal and ethical literacy: Knowledge of the legal requirements and ethical considerations surrounding using restraints.
- Communication skills: Employing verbal and non-verbal communication strategies to engage with individuals respectfully and effectively.
- Risk assessment: Identifying situations where restrictive practices might be considered necessary.
How to Assess Staff Competency in Minimising Restrictive Practices
Assessing staff competency is a structured process that ensures healthcare professionals have the necessary skills and knowledge to minimise restrictive practices. The following table illustrates key competencies and methods of assessment:
| Competency | Assessment Method |
|---|---|
| Understanding of policies related to restrictive practices | Written assessment and discussion based learning |
| Identification of behaviours and potential triggers | Case study |
| De-escalation techniques | Role-playing scenarios |
| Use of alternative interventions | Direct observation in practice |
| Adherence to ethical and legal frameworks | Review of decision-making in hypothetical situations |
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Reinforce and Develop Restrictive Practice Minimisation Skills
Healthcare organisations can implement a range of strategies to support skill development in minimising restrictive practices. These include:
- Regular interactive workshops and simulations to practice de-escalation and alternative interventions.
- Peer mentoring and coaching programs for sharing experiences and knowledge.
- Reflective practice sessions to discuss real cases and learn from decisions made.
- Continuous professional development opportunities focusing on person-centred care and rights-based approaches.
- Engagement with external experts for specialised training and insights.
Sample Training Plan for the Restrictive Practice Training Requirement
The ability of staff to minimise restrictive practices is essential, and can be improved through an effective training program upon identifying the areas of lacking skills (via needs assessments).
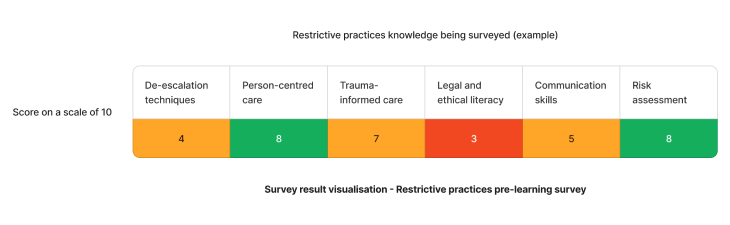
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example, the skill needed for restrictive practice minimisation that requires the most attention is legal and ethical literacy. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps and enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Legal and ethical literacy |
|
Need an LMS that can support minimising restrictive practice training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your restrictive practice minimisation training requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Minimising Restrictive Practices - Example
The following questions can be utilised within surveys to assess staff's capabilities in minimising restrictive practices:
Staff Survey - Minimising Restrictive Practices Competency
-
Can you describe the decision-making process you follow before considering the use of a restrictive practice?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you ensure compliance with the NSQHS and Aged Care Quality Standards when implementing restrictive practices?
- [Answer here]
-
Provide an example of an alternative strategy you have used to avoid the use of a restrictive practice.
- [Answer here]
-
How do you stay informed about the least restrictive options for managing patient behaviour?
- [Answer here]
-
In your experience, what is the most challenging aspect of minimising restrictive practices, and how do you address this challenge?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Ensuring the minimisation of restrictive practices is a complex but essential component of quality healthcare provision. Through targeted training, skill development, and ongoing competency assessments, healthcare organisations can empower their staff to make informed, ethical decisions.
References
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care, 2023. 'Restrictive practices in aged care – a last resort'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS - Comprehensive Care Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.35'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.36'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Standard 3. Personal and Clinical care'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Requirement 3.3 (a)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 3.2.7'



