What is Partnering with Consumers?
Partnering with consumers involves engaging patients and their families in the design and delivery of healthcare services. It's a collaborative approach that empowers consumers to be active in their care, ensuring services are tailored to meet their needs and preferences.
The Importance of Partnering with Consumers

Understanding the significance of partnering with consumers is pivotal in healthcare, where patient-centred care is increasingly recognized as a key component of quality service. This expanded section delves into why this partnership is not just beneficial, but essential:
- Improved Health Outcomes: Active patient participation in their own care leads to better health outcomes. Patients who are engaged in their treatment plans are more likely to adhere to recommendations and actively manage their health.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: Partnering with consumers ensures that healthcare services are more responsive to the needs and preferences of patients, leading to higher levels of patient satisfaction and trust.
- Informed Decision Making: When patients are partners in their healthcare journey, they are better informed about their conditions and treatment options. This leads to more effective shared decision-making.
- Increased Patient Safety: Engaging patients in their care can lead to a reduction in medical errors. Patients who understand their treatments and medications are more likely to notice and report potential errors or adverse effects.
- Healthcare System Efficiency: Patient engagement can lead to more efficient use of healthcare resources. When patients are involved in their care planning, it can result in fewer unnecessary tests, reduced hospital admissions, and more effective management of chronic diseases.
- Cultural Competency: Partnering with consumers from diverse backgrounds helps in understanding cultural specificities, leading to more culturally competent and sensitive healthcare provision.
- Regulatory Compliance: In many regions, including Australia, partnering with consumers is a regulatory requirement. It ensures compliance with standards set by bodies like the NSQHS and ACQS.
- Innovation and Service Improvement: Feedback and insights from patients can drive innovation and continuous improvement in healthcare services.
What is the "Partnering with Consumers" Training Requirement?
Staff training in this area focuses on understanding the principles of consumer partnership, effective communication, and strategies for involving consumers in care planning and decision-making processes.
Relevant Standards
Action 3.04: Partnering with consumers - Preventing and Controlling Infections Standard
Organisational processes are in place and clinicians are consistent with the Partnering with Consumers Standard when assessing risks and preventing and managing infections, and implementing the antimicrobial stewardship program to:
- Actively involve patients in their own care
- Meet the patient’s information needs
- Share decision-making
Action 4.03: Partnering with consumers - Medication Safety Standard
Clinicians use organisational processes from the Partnering with Consumers Standard in medication management to:
- Actively involve patients in their own care
- Meet the patient’s information needs
- Share decision-making
Action 5.03: Partnering with Consumers - Comprehensive Care Standard
Organisational processes for clinicians to use from the Partnering with Consumers Standard when providing comprehensive care to:
- Actively involve patients in their own care
- Meet the patient’s information needs
- Share decision making
Action 7.03: Partnering with consumers - Blood Management Standard
Clinicians use organisational processes from the Partnering with Consumers Standard when providing safe blood management to:
- Actively involve patients in their own care
- Meet the patient’s information needs
- Share decision-making
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 2.3 (c): Assesment and planning
is based on ongoing partnership with the consumer and others that the consumer wishes to involve in assessment, planning and review of the consumer’s care and services
Action 1.1.4: Developing Professional and trusting relationships
Workers have professional and trusting relationships with older people and work in partnership with them to deliver care and services.
Action 2.1.1: Developing direct client partnerships
The governing body directly partners with older people to set priorities and strategic directions forthe way care and services are provided.
Action 2.1.2: Partnerships - supporting and partnering with clients
Meaningful and active partnerships with older people inform organisational priorities and improvements to quality care and services.
Action 2.1.3: Client Partnerships - Organisation governance
The provider partners with older people in the governance of the organisation and the design, evaluation and improvement of quality care and services.
Action 2.1.5: Partnering carers with people in diverse and high-risk groups
The provider partners with older people that reflect the diversity of those who use their services.
Action 3.1.2: Involving clients in planning and assessments
Assessment and planning are based on ongoing communication and partnership with the older person and others that the older person wishes to involve.
Action 3.2.6: Dementia care
c) The provider implements a system for caring for older people living with dementia that enables family, carers and health professionals involved in the older person’s care to act as partners in planning and delivering the older person’s care (in line with the older person’s wishes).
Action 3.4.1: Identifying others involved in client care
The provider, in partnership with the older person, identifies others involved in the older person’s care and ensures coordination.
Action 3.4.2: Recognising and involving carers
Carers are recognised as partners in the older person’s care and involved in the coordination of care and services.
Action 6.3.1: Developing and reviewing menus (with clients)
a) Menus (including for texture modified diets) are designed in partnership with older people
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Staff Skills Required for Partnering with Consumers
Effective partnering with consumers extends beyond basic communication skills. Healthcare professionals need a varied skill set to engage meaningfully with patients and their families. These skills can be categorised as follows:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Empathy and Compassion | Understanding and sharing the feelings of patients, showing genuine concern for their experiences and wellbeing. |
| Cultural Competency | Ability to understand, communicate with, and effectively interact with people across cultures, respecting their beliefs and practices. |
| Active Listening | Fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what the patient says. |
| Patient Advocacy | Supporting patients' rights and preferences in healthcare settings, ensuring their voices are heard and respected. |
| Conflict Resolution | Effectively managing and resolving misunderstandings or disagreements with patients or their families. |
| Health Literacy Promotion | Enhancing patients' understanding of health information to make informed decisions about their care. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Partnering with Consumers
To ensure staff are proficient in partnering with consumers, regular assessments are necessary. The following methods can be used for assessment:
- Direct Observation: Supervisors or peers observe interactions with patients, focusing on the application of key skills.
- Feedback from Patients: Collecting feedback through surveys or interviews to gauge patient satisfaction and staff effectiveness.
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging staff to reflect on their skills and identify areas for improvement.
- Role-Playing Exercises: Simulating scenarios where staff can demonstrate their ability to partner with patients.
- Knowledge Tests: Assessing understanding of best practices and policies related to patient partnership.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Develop Skills in Partnering with Consumers
Developing staff skills in partnering with consumers involves a strategic approach. The following strategies can be employed:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Workshops and Seminars | Organising educational sessions focusing on the development of specific skills such as cultural competency, empathy, and conflict resolution. |
| Mentoring and Peer Support | Pairing less experienced staff with seasoned mentors for guidance and support in real-world situations. |
| Online Learning Modules | Utilising digital platforms to offer accessible and flexible learning opportunities, including interactive scenarios and case studies. |
| Continuous Feedback Mechanisms | Implementing regular performance reviews and feedback sessions to provide constructive criticism and praise. |
| Role-Playing and Simulation | Creating realistic scenarios for staff to practice and refine their skills in a controlled environment. |
| Collaboration with Consumer Groups | Engaging directly with consumer advocacy groups to gain insights and integrate their perspectives into training programs. |
Sample Training Plan for the Partnering with Consumers Requirement
A structured training plan is essential for developing skills in for the partnering with consumers requirement.
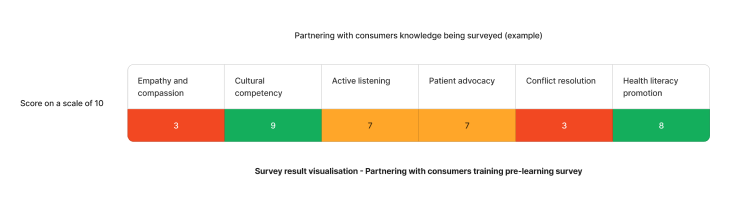
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skill requiring the most attention for partnering with consumers are empathy and compassion and conflict resolution. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Empathy and compassion | |
| Q2 | Conflict resolution |
Need an LMS that can support staff partnering with consumers?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Partnering with Consumers - Example
To evaluate an individual's skills in operating partnering with consumers, consider using these survey questions:
Staff Survey - Partnering with Consumers Competency
-
How effectively do you feel you communicate with patients?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you provide an example of how you have involved a consumer in the decision-making process?
- [Answer here]
-
How comfortable are you with handling diverse patient needs and preferences?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe a situation where you demonstrated empathy in a patient interaction.
- [Answer here]
-
How do you stay informed about the best practices in consumer partnering?
- [Answer here]
-
Rate your ability to work collaboratively with consumers and their families.
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Developing a robust training program for partnering with consumers is vital in meeting healthcare standards and providing high-quality, patient-centred care. By focusing on key skills and ongoing staff development, healthcare organisations can ensure they are effectively meeting the needs of their consumers.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'Partnering with Consumers Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.04'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 4.03'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.03'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 7.03'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. Aged Care Quality Standards, 'Requirement 2.3(c)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 1.1.4, 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3, 2.1.5, 3.1.2, 3.2.6(c), 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 6.3.1(a)'



