What is Infection Prevention?
Infection prevention is a set of protocols and practices aimed at reducing the risk of transmitting infections within healthcare settings. This includes measures such as effective hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilisation of equipment, and proper waste disposal (Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2019).
What is the ACQSC Infection Prevention Training Requirement?
The Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission (ACQSC) has outlined specific requirements for infection prevention training under Requirement 3.3(g) and Action 4.2.1 and 4.2.2 of the Strengthened Aged Care Standards. The aim is to ensure that healthcare workers are equipped with the essential knowledge and skills to minimise the risk of infection (Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2021).
Relevant Standards
Requirement 3.3 (g): Minimising infection-related risks by implementing:
- Standard and transmission based infection prevention safeguards
- Antibiotic prescribing and use practices for optimal care and antibiotic resistance reduction mechanisms
Action 4.2.1: Infection prevention system needs
The infection prevention system effectively:
- a. Appoints a suitably credentialed and trained lead for infection prevention and control.
- b. Outlines both standard and setting-specific transmission-based precautions, encompassing cleaning procedures, hand sanitation methods, respiratory hygiene, cough etiquette, and the management and disposal of waste.
- c. Places a premium on safeguarding the rights, health, safety, and overall well-being of elderly individuals.
- d. Adheres to up-to-date, evidence-informed best practices.
- e. Incorporates extra measures for immediate response to emerging viruses and confirmed or suspected outbreaks of infectious illnesses.
- g. Effectively communicates and controls infection risks for the elderly, as well as their families, caregivers, and healthcare workers.
- h. Takes into account data on immunisation and infection rates among healthcare workers and older individuals when making decisions.
Action 4.2.2: Infection prevention systems application
The infection prevention and control system is implemented and ensures:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) is available to those that may need it (notably workers and older people)
- Correct use of PPE is supported and communicated to those that require it
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the ACQSC infection prevention and control training requirement
Infection Prevention Skills Staff Need for ACQSC Compliance
Healthcare staff need a diverse set of skills to comply fully with the ACQSC standards on infection prevention. The following elaborates on the essential skills required:
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Correct techniques for handwashing and using hand sanitiser |
| PPE Utilisation | Proper donning and doffing of PPE, including masks, gloves, and gowns |
| Waste Management | Proper disposal of healthcare waste including sharps, biological waste, and general waste |
| Equipment + Facility Sterilisation | Knowledge of how to sterilise medical equipment and facilities |
| Infection Identification | Ability to identify signs of infections in patients and colleagues |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Infection Prevention (ACQSC)
Infection prevention and control competency can be assessed through a multi-method approach:
- Observation: Supervisors should observe staff performing tasks to ensure that they are following protocols.
- Simulation Exercises: Simulated scenarios can be used to test staff reaction to various infection risks.
- Written Assessments: Quizzes or multiple-choice questions related to infection prevention.
- Feedback: Peer and self-assessment through anonymous surveys or one-on-one evaluations.
- Auditing: Routine audits of infection control practices can provide quantitative data on compliance.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Improve Infection Prevention Skills for the ACQSC standard
Multiple strategies can support employees in developing these crucial skills:
- Continued Education: Offer periodic refresher courses that are up-to-date with the latest guidelines.
- Simulation Drills: Conduct real-time simulation exercises to emulate emergency scenarios.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for anonymous feedback regarding infection prevention protocols.
- Mentorship Programs: More experienced staff can mentor newer employees in infection control best practices.
- Resource Availability: Ensure that staff has access to the necessary resources including PPE and sanitisation supplies.
Sample Training Plan for the Infection Prevention (ACQSC) Training Requirement
Ensuring staff are competent in the relevant skills is pivotal to facilitating best-practice infection prevention and control.
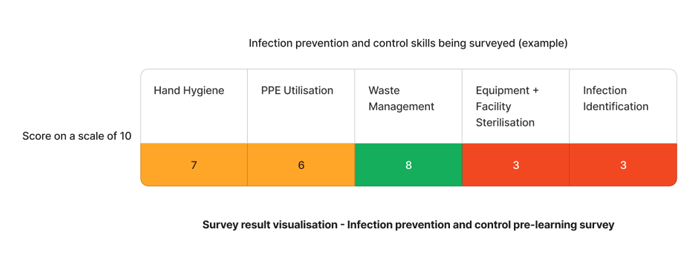
Using the above survey as an example - The skills that requires the most attention are equipment + facility sterilisation and infection identification skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Infection Identification | |
| Q2 | Equipment + Facility Sterilisation |
Need an LMS that can support infection prevention learning?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your infection prevention and control requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Infection Prevention (ACQSC Standards) - Example
The following is an example survey that learning and development coordinators may use to asses staff competency on clinical assessment.
Staff Survey - Infection Prevention Competency
-
How often should you perform hand hygiene?
- [Answer here]
-
What is the correct sequence for donning PPE?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you dispose of sharps?
- [Answer here]
-
What steps are involved in sterilising equipment?
- [Answer here]
-
What are the signs of a healthcare-associated infection?
- [Answer here]
-
What are the reporting procedures for an infection breach?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
In summary, adhering to ACQSC guidelines on infection prevention is vital for both compliance and the well-being of older adults in healthcare settings. A comprehensive training program and ongoing assessments are key to equipping staff with essential skills. Through continuous education and effective communication, healthcare organisations can create a safe and efficient environment that prioritises patient health.
References
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Aged Care Quality Standard - Personal and clinical care - 3.3 (g)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 4.2.1-4.2.2'



