What is Induction Training?
Induction is the formal process of introducing a new employee to an organisation and providing them with critical information about workplace culture, policies and expectations.
Induction training, which is a compulsory part of this process, equips new employees with the essential knowledge and skills required to perform their roles safely and effectively (Safe Work Australia 2024). Induction activities typically include an overview of health and safety regulations, job-specific duties, organisational policies and procedures and introductions to team members and management. This enables new starters to understand how to work within the organisation’s specific context, safely and effectively from day one.
What are the Benefits of Induction Training?
When delivered effectively, induction training ensures that all safety and regulatory standards, such as those outlined in the Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Act 2004, are met. Furthermore, a positive onboarding experience, which includes induction, has a direct impact on employee productivity and safety. Research from the Australian Government Department of Employment and Workplace Relations highlights that up to 20% of employee turnover occurs within the first 45 days, emphasising the importance of effective induction to retain talent and reduce recruitment costs.
Defining Key Terms
Several terms are used across the industry, some of which are interchangeable. We’ll define them for clarity, but it’s important not to get too caught up in the terminology, as the concepts often overlap.
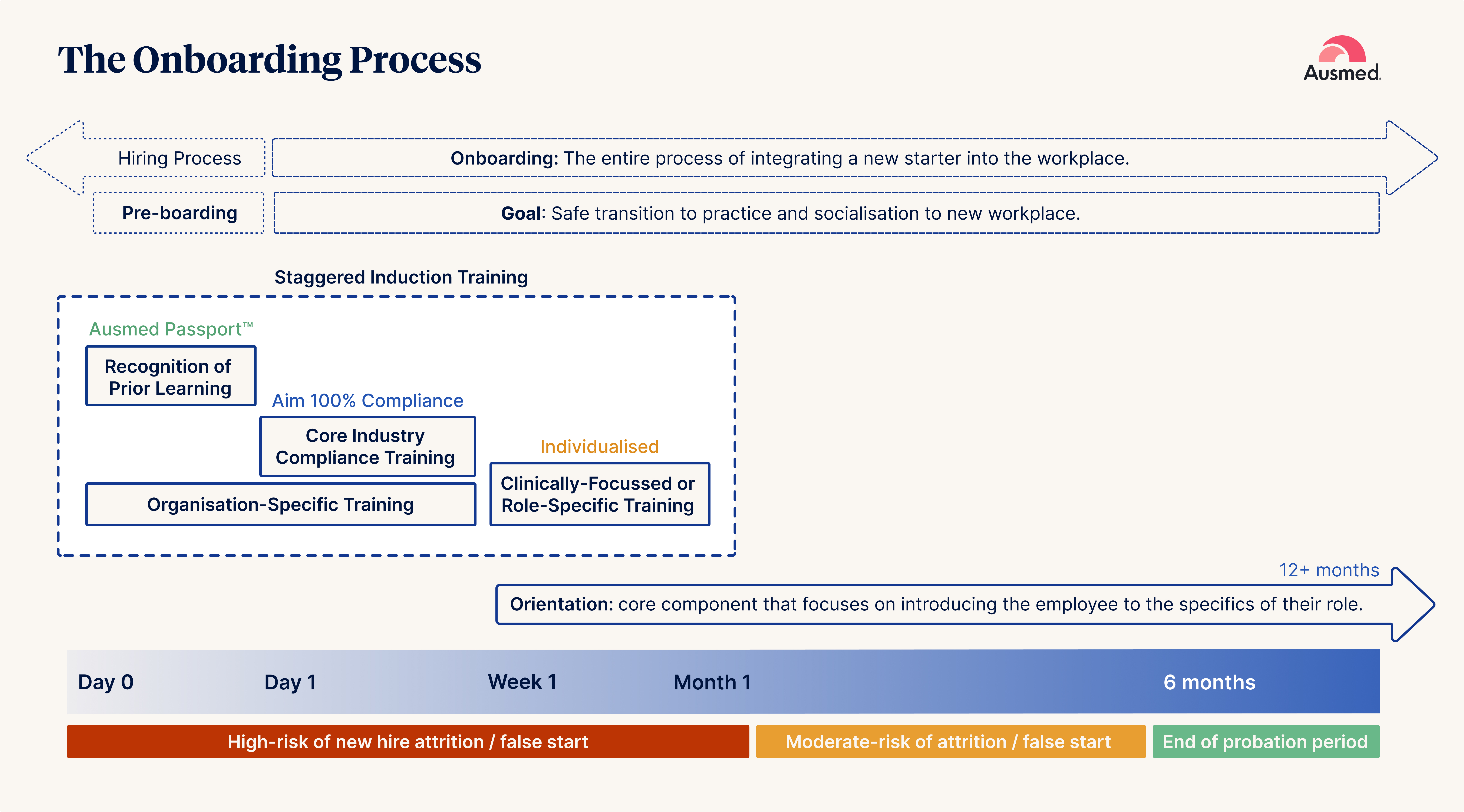
Onboarding is the entire process of integrating an employee, beginning with a job offer and continuing until the end of the probation period, which is usually six months.
Orientation is a core component of onboarding that focuses on introducing the employee to the specifics of their role. The most effective organisations onboard new starters for the duration of their first year - their most vulnerable period (Carucci 2018).
Transition to practice refers to the process where individuals, whether they have completed formal qualifications like degrees or vocational training such as a Certificate III or IV, move from education or initial training into competent, independent practice within the workplace (Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care 2023).
A transition-to-practice program provides an evidence-based framework of support, often lasting 12 months, to help individuals develop their skills in real-world settings. This process is not limited to new staff; it can also support existing staff who are transitioning to new roles, ensuring they receive the mentorship, guidance and resources necessary to perform their duties effectively and confidently (Australian Primary Care Association n.d.; Russell et al. 2023).
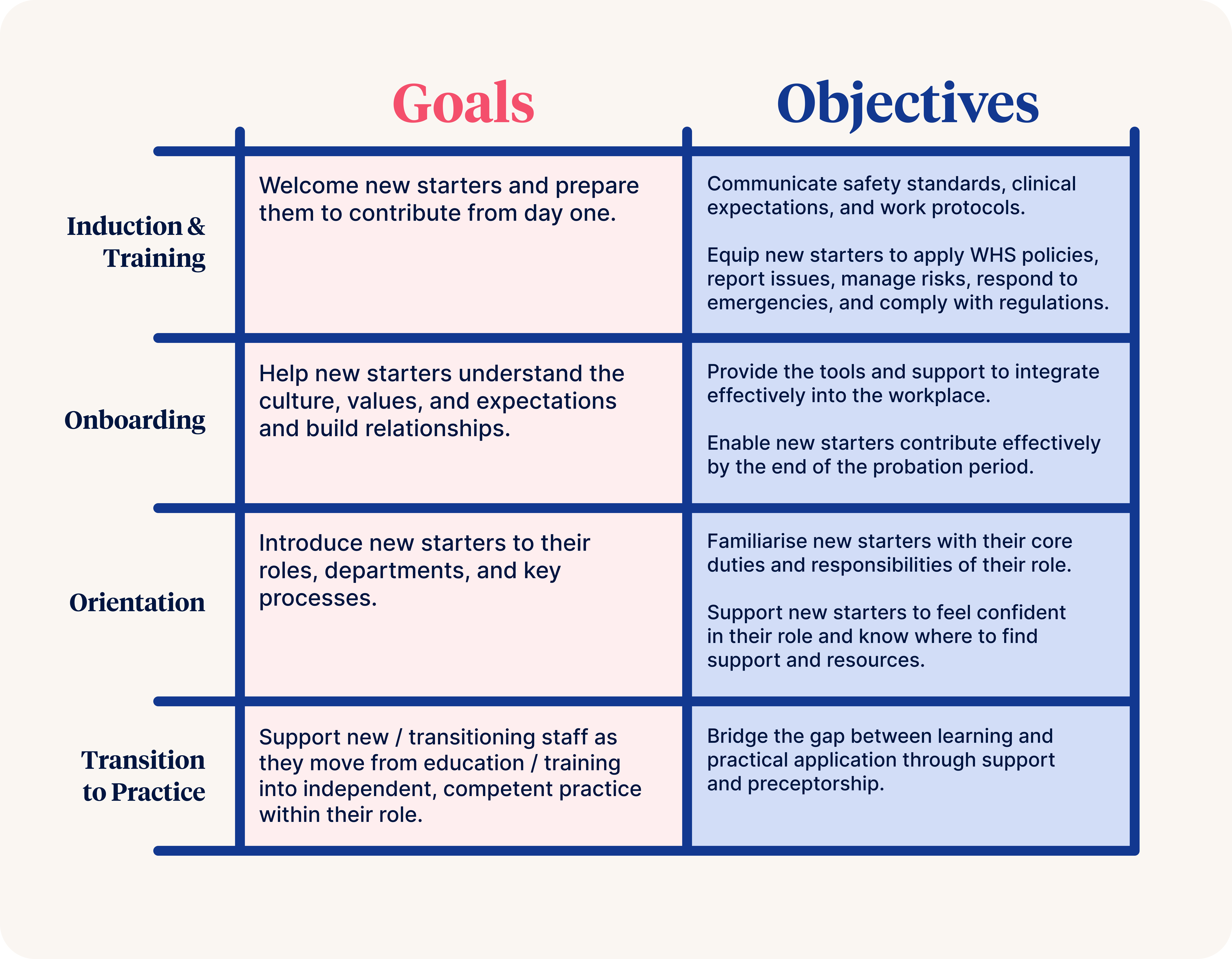
This table outlines the goals and objectives of Induction, Onboarding, Orientation, and Transition to Practice.
What are the Relevant Legislation and Standards Related to Induction Training?
Make sure that you know about your responsibilities under the Fair Work Act 2009:
- 10 National Employment Standards (NES)
- Awards and agreements
- Wages
- Discrimination
- Record keeping and pay slips
- Taxation and superannuation
- Workplace health and safety
- Workers compensation
As an employer, you are responsible for providing a healthy and safe working environment. In addition to the Fair Work Act 2009, there are several Acts and standards relevant to induction training.
Acts
- Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Act 2004 (Vic): Requires employers to provide adequate training, supervision and information to ensure employees’ safety at work.
- Aged Care Act 1997 (Cth): Mandates appropriate training and development for workers in aged care settings.
- Work Health and Safety (WHS) Act 2011 (Cth): Enforces safety obligations for all Australian workplaces, requiring effective induction training.
National Standards:
- Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards: Outcome 2.9 Human Resource Management states that workers must be provided with training and supervision to perform their roles effectively.
- National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards: Leaders are responsible for continuous improvement in safety and quality. Action 1.19 requires health service organisations to provide orientation on safety and quality roles and responsibilities to governing bodies, clinicians and all staff, including contractors, locums, students and volunteers.
- National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) Practice Standards: Under Provider Governance and Operational Management, a system must be in place to identify, plan, facilitate, record and evaluate worker training. This ensures that staff meet participant needs and includes mandatory training on obligations under the NDIS Practice Standards and other NDIS rules.
While these laws and standards outline the importance of training and supervision, they generally do not specify the exact modules that must be included in a training plan. Organisations must interpret, contextualise and apply these requirements to suit their specific staff, roles and circumstances.
What Should Induction Training Focus on?
Induction training should focus on three core matters:
- Core Industry Compliance Training, including:
- Workplace Health and Safety (WHS)
- Incident Reporting
- Clinical Safety
- Emergency Procedures
- Legislative Compliance
- Organisation-Specific Training
- Clinically-Focused or Role-specific Training
.png)
Core Industry Compliance Training
These are common core industry compliance training items often included in induction plans, but they may vary depending on your requirements. To help plan what core industry compliance items your organisation and new starters require, it's helpful to consider the desired learning outcomes first (New Hire Outcome). Understanding what we want the new hire to know, be able to do or practice helps confirm the focus on what topics are mandatory for induction and which may be ‘nice to have’.
| Focus | New Hire Outcome | Ausmed Training Module | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workplace Health and Safety (WHS) | New starters will be able to understand and apply workplace health and safety (WHS) policies to maintain compliance and a safe work environment. | Work Health and Safety | 30 min |
| Bullying, Harassment & Discrimination in the Workplace | 25 min | ||
| Manual Handling | 14 min | ||
| Cyber Security | 20 min | ||
| Fire Safety | 23 min | ||
| Open Disclosure and Apology | 22 min | ||
| Incident Reporting | New starters will be able to report any safety issues accurately and will understand the relevant roles and responsibilities. | Incident Report Writing | 9 min |
| Clinical Safety | New starters will be able to identify and minimise healthcare-specific hazards and clinical risks to themselves and their clients/patients. | Hand Hygiene Essentials | 23 min |
| Infection Prevention and Control* | 28 min | ||
| Choking Management* | 20 min | ||
| Food Safety* | 28 min | ||
| Emergency Procedures | New starters will be able to effectively respond to emergencies by understanding and following the organisation’s emergency protocols. | Basic Life Support | 32 min |
| Legislative Matters: Aged Care | Aged Care / Home Care: New starters will be able to demonstrate an understanding of relevant healthcare legislation and standards and apply them in their day-to-day responsibilities. | Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards (all) | 30 min |
| Charter of Aged Care Rights and Code of Conduct (Care staff only) | 25 min | ||
| SIRS (RN/EN/Management only) | 40 min | ||
| Minimising Restrictive Practices in Aged Care | 25 min | ||
| Legislative Matters: Acute Care | Acute Care: New starters will be able to demonstrate an understanding of relevant healthcare legislation and standards and apply them in their day-to-day responsibilities. | National Safety and Quality Health Care Standards | 25 min |
| Minimising Restrictive Practices in Healthcare Settings | 31 min | ||
| Legislative Matters: Disability Care | Disability Care: New starters will be able to demonstrate an understanding of relevant healthcare legislation and standards and apply them in their day-to-day responsibilities. | NDIS Practice Standards: Core Module | 22 min |
| The NDIS Code of Conduct | 24 min | ||
* Denotes a role-specific requirement only. Ensure that any items relating to legislative matters are sector-specific to your relevant Standards'.
Core Industry Compliance Training
So we’ve covered the core industry compliance training, what about organisation-specific training? These are common organisation-specific items often included in induction plans, but they will vary depending on your requirements. The format and duration will depend on whether the training is delivered face-to-face or online.
- Organisation policies and procedures
- Technology and systems (LMS, CIS/EMR, payroll, incident reporting tools)
- Team roles and responsibilities
- Communication and escalation protocols (i.e. ISOBAR)
- Quality improvement initiatives
- Client/resident and patient care pathways
It is important to keep this list of organisation-specific items manageable and to assist with managing training fatigue and educator or facilitator workloads.
Clinical-Focused and Role-Specific Induction Topics
Clinically-focused and role-specific induction topics should focus on the key responsibilities and skills required for different roles within your organisation. Spacing these out allows staff to apply what they have learned while gradually increasing their responsibilities
Here are common examples of clinical-focused and role-specific induction topics for care staff and Registered and Enrolled Nurses:
Care Worker
- Recognising Deterioration: Care Workers
- Medication Prompting, Assistance and Administration for Care Workers
- Skin Integrity and Pressure Injuries: Care Workers
- Falls Prevention and Management: Care Workers
- Dysphagia and the IDDSI Framework
- Dementia and Understanding Behavioural Changes
- Supporting Activities of Daily Living: Continence and Toileting
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care: Care Workers
- Promoting Mental Health and Wellbeing in Aged Care
Registered and Enrolled Nurses
- Recognising and Responding to Clinical Deterioration
- Wound Assessment
- Wound Dressing
- Phlebotomy
- Central Venous Access Devices (CVADs)
- Managing Urinary Catheters in Acute Settings
- Insulin Therapy
What are the Challenges of Induction Training?
While induction training is essential for ensuring compliance and safety, the process is not without its obstacles. Induction training presents several challenges that affect both new staff and organisations, particularly L&D or Education and Human Resource teams. Recent benchmarking by Ausmed has highlighted eight key themes that encompass the major challenges of induction training.
- Time constraints
- Content overload
- Compliance requirements
- Staff engagement
- Coordination
- Relevancy
- Consistency
- Supporting socialisation
.png)
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Time constraints | Limited time is available for staff and the organisation to complete induction training. The long length and high frequency of induction training are challenging, as there is a continual need to onboard new staff quickly and efficiently. |
| Content overload | Content overload occurs when too much information is delivered in a short period, making it difficult for new starters to absorb. |
| Compliance requirements | A lack of knowledge and alignment between teams on how to consistently ensure that the relevant regulatory requirements of induction training are met. |
| Staff engagement | Low engagement due to excessive requirements can result in boredom and lack of focus and may impact new starters’ commitment to the new organisation. Staff engagement reflects the level of interest and motivation new starters have during induction, which can be affected by the quality, quantity, and method of training delivery. |
| Coordination | Managing schedules, resources, and facilitators to ensure efficient training delivery, often across multiple sites, is challenging. Aligning departments, coordinating speakers, and fitting training sessions within operational demands without disrupting service delivery can be difficult. |
| Relevancy | Relevancy refers to how well induction training content aligns with the specific needs of new staff in their roles. It also highlights the ongoing need to keep training materials updated to reflect best practices and regulatory requirements. |
| Consistency | Consistency ensures that all employees receive the same quality and level of training, regardless of location, department, or shift. Inconsistent training can lead to discrepancies in skills, knowledge, and adherence to organisational policies, making standardised training processes essential for maintaining alignment and quality of care. |
| Supporting socialisation | Supporting socialisation involves helping new starters integrate into the organisational culture, build relationships, and feel a sense of belonging. This process is facilitated through buddy systems, mentorship programs, and encouraging interaction with team members and leadership. A lack of time and resources for this crucial step can leave new starters feeling unsupported, impacting their short- and long-term success. |
What’s the Impact of These Challenges?
The challenges of induction training have significant impacts on both new staff and organisations. For new hires, time constraints and content overload can lead to rushed training, poor knowledge retention, and disengagement. This results in frustration, training fatigue, and skill gaps, ultimately affecting their ability to perform effectively in their roles.
For organisations, these issues lead to higher costs, reduced productivity, delayed onboarding, and increased risk. Furthermore, poor coordination, relevancy, and consistency in training can result in operational disruptions, variations in performance, and higher turnover rates due to disengaged or poorly prepared staff.
The Importance of Benchmarking
Benchmarking induction training data helps organisations compare training structures across sectors, revealing efficiencies or gaps. This can reduce training fatigue, enhance engagement and ensure compliance while improving onboarding. It also highlights sector-specific trends, enabling organisations to tailor your induction strategies to meet standards and adapt to evolving regulatory requirements.
Recent benchmarking by Ausmed has highlighted current approaches to induction training, with a focus on two core data points:
Average Number of Resources in Training Plan
Guide+Image1.png)
Average Training Plan Length (Hours)
Guide+Image+2.png)
.png)
Are your new starters suffering from training fatigue?
If you believe your current induction training plan may be excessive in duration, please contact us for assistance.
Streamlining Induction Training
To effectively streamline induction training, three key strategies can be implemented: (1) Mindset, (2) Staggered Training, and (3) Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL).
1. Mindset
While induction training is essential, it is just one piece of a larger transition-to-practice program. Rather than expecting induction to cover everything a new staff member needs to know, the focus should be on core regulatory requirements. Success comes from combining induction with a broader orientation and transition strategy that includes upskilling, cross-skilling, and supporting new staff in their progress towards full competence, especially in clinical roles.
2. Staggered Training
Streamlining the induction process through a staggered approach helps manage information overload. By prioritising regulatory essentials first, followed by organisational needs and role-specific training, new starters can absorb information more effectively. This approach is complemented well when broader socialisation strategies and using creative, low-cost initiatives are included to foster a welcoming environment.
What is Staggered Induction Training?
Staggered learning refers to spreading out the delivery of training over some time rather than cramming all the content into the first few days. We're seeing organisations gain the following results with this approach:
- Lower disengagement and training fatigue
- Reduced the risk of new hire attrition or a false-start
- More effective and supported transition to practice
- Improved management of the clinical facilitator/educator workload
Click here to watch a recording of an Ausmed webinar on Streamlining Induction where Zoe explains staggered learning in more detail.
3. Recognition of Prior Learning
Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) tools like Ausmed Passport™ enable organisations to acknowledge the training new starters have already completed, avoiding redundant training and reducing onboarding time and costs. By eliminating repetitive modules, RPL speeds up the induction process, helping staff start work sooner with confidence.
What is the Ausmed Passport™?
The Ausmed Passport™ is a free digital certificate that fast-tracks induction by recognising prior learning (RPL) and standardises eight core mandatory training areas in aged care. It enables a staff member to carry it with them from one employer to the next to evidence that they have completed mandatory training relevant to and recognised by the sector. It is currently available as an Aged Care Training Passport only.
Why we Created the Ausmed Passport™
We created Passport™ because we believe that all training should be as impactful as possible. By providing common training items free to all sector participants, we can support the aged care sector to focus their learning and development resources and employee time more efficiently on initiatives that will positively impact their organisations - and especially - the unique care needs of older people.

How can your organisation benefit?
Click here for more info about the Ausmed Passport™ including an ROI Calculator to assess what impact Ausmed Passport™ could have on your organisation.
How Does the Ausmed Passport™ Work?
Ausmed Passport™ is completely free for both individuals and organisations to use in just three simple steps: Learn, Share, and Verify.

Please reach out if you want to explore using the Ausmed Passport™ within your organisation.
Supporting Socialisation to a New Workplace
How can we help new starters feel highly valued as they transition to practice? There are some impactful things we can do that don't require significant resources but can significantly improve engagement and reduce the impact of challenges during the onboarding process. Have you thought about these low-to-no cost ideas?
- Personalised Welcome Pack: Include a simple note from the manager or team to create a sense of belonging from day one.
- Lunch with the Manager: Encourage dedicated catch-ups during paid breaks to build rapport and help new starters feel valued.
- Peer-led Q&A: Informal sessions with experienced staff provide practical advice in a relaxed setting, like during scheduled breaks.
- Social Buddy: Pair new starters with a ‘social buddy’ to help them navigate the team and culture outside formal training.
- Recognition for Small Wins: Acknowledge early successes with a thank-you note or shoutout to boost morale.
- Open Door Times: Set designated times when managers are available for questions, creating a supportive environment.
Successful Induction Training
Here is a useful checklist to ensure your induction training program is effective and engaging and minimises unnecessary training costs.
.png)
References and Useful Resources
For more information, see our Induction Training - FAQs. This quick read offers quick insights into essential aspects of induction training, from its purpose and benefits to the challenges and solutions to streamline induction
- Aged Care Act 1997 (Cth)
- Occupational Health and Safety Act 2004 (Vic)
- Safe Work Australia 2024, National Safe Work Month, Australian Government, viewed 3 September 2024, https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/national-safe-work-month/week-1
- Department of Health 2024, Transition to Practice Program, Australian Government, viewed 5 September 2024, https://www.health.gov.au/our-work/transition-to-practice-program
- Department of Employment and Workplace Relations 2022, Onboarding, Australian Government, viewed 8 September 2024, https://www.dewr.gov.au/employing-and-supporting-women-your-organisation/inclusive-recruitment/onboarding
- Fair Work Ombudsman 2024, A guide to hiring new employees, Australian Government, viewed 30 September 2024, https://www.fairwork.gov.au/sites/default/files/migration/712/A%20guide%20to%20hiring%20new%20employees.pdf
- Australian Primary Health Care Nurses Association 2024, Transition to Practice Program, APNA, viewed 8 September 2024, https://www.apna.asn.au/education/TransitiontoPracticeProgram
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care 2021, NSQHS Standards, Australian Government, viewed 10 September 2024, https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/standards/nsqhs-standards
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission 2024, Supporting People Who are Visitors to Your Service, Australian Government, viewed 6 September 2024, https://www.agedcarequality.gov.au/resource-library/supporting-people-who-are-visitors-your-service-training-resource-aged-care-workers
- Department of Health 2024, Support and Training for Aged Care Volunteers, Australian Government, viewed 7 September 2024, https://www.health.gov.au/topics/aged-care/volunteers/support-and-training
- Ausmed Education 2023, Ausmed Passport, Ausmed Education, viewed 2 September 2024, https://www.ausmed.com.au/passport
- Ausmed Education 2023, Ausmed Passport for Organisations, Ausmed Education, viewed 9 September 2024, https://www.ausmed.com.au/passport/organisations
- Youl, Z 2024, ‘Guide to Mandatory Training’, L&D Toolbox, 19 June, viewed 12 September 2024, https://www.ausmed.com.au/organisations/toolbox/guides/guide-to-mandatory-training
- NDIS Quality and Safeguards Commission 2024, NDIS Practice Standards and Quality Indicators, Australian Government, viewed 11 September 2024, https://www.ndiscommission.gov.au/sites/default/files/2024-05/ndis-practice-standards-and-quality-indicatorsfinal1_1.pdf
- The Skills Centre 2024, Online Health and Safety Courses, The Skills Centre, viewed 13 September 2024, https://theskillscentre.co.uk/courses-services/eskills/online-health-safety-courses
- Piccolo, K 2024, ‘Checklist for Onboarding New Employees’, Genesis HR Solutions Blog, 22 March, viewed 15 September 2024, https://genesishrsolutions.com/peo-blog/checklist-for-onboarding-new-employees/
- Drake International 2024, The Cost of Employee Turnover Calculator, Drake International, viewed 18 September 2024, https://au.drakeintl.com/clients/calculate-staff-turnover
- Russell, K, Coventry, T, Tamaliunas, S & Juliff, D 2023, ‘Graduate Nurse Education Programs: Transition Pathway for Registered Nurse Employment’, OJIN: The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, vol. 28, no. 2, viewed 14 September 2024, https://ojin.nursingworld.org/table-of-contents/volume-28-2023/number-2-may-2023/articles-on-previously-published-topics/graduate-nurse-education-programs/
- Kurnat-Thoma, E, Ganger, M & Channell, L 2017, ‘Reducing Annual Hospital and Registered Nurse Staff Turnover—A 10-Element Onboarding Program Intervention’, SAGE Open Nursing, viewed 9 September 2024, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2377960817697712
- Young-Brice, A, Farrar-Stern, K & Malin, M 2022, 'Comprehensive Onboarding and Orientation to Support Newly Hired Faculty in a Nursing Program', Nurse Educator, vol. 47, no. 6, pp. 347-351, viewed 30 September 2024, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35816199/
- Hall, S, Taylor, S & Altobar, C 2019, 'Transition to Practice: Onboarding Components for Establishing and Sustaining Healthy Work Environments', AACN Advanced Critical Care, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 416-420, viewed 30 September 2024, https://europepmc.org/article/med/31951662
- Valdes, EG, Sembar, MC & Sadler, FMJ 2023, 'Onboarding New Graduate Nurses Using Assessment-Driven Personalized Learning to Improve Knowledge, Critical Thinking, and Nurse Satisfaction', Journal for Nurses in Professional Development, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 18-23, viewed 30 September 2024, https://journals.lww.com/
- Wright, D 2018, The Ultimate Guide to Competency Assessment in Health Care, 3rd edition, Creative Health Care Management, Minneapolis, MN.
- Harper, M (ed.) 2022, Core Curriculum for Nursing Professional Development, 6th edition, Association for Nursing Professional Development, Chicago, IL.
- Harper, M & Maloney, P (eds.) 2022, Nursing Professional Development Scope & Standards of Practice, 4th edition, American Nurses Association, Silver Spring, MD.
Author
Zoe Youl
Zoe Youl is a Critical Care Registered Nurse with over ten years of experience at Ausmed, currently as Head of Community. With expertise in critical care nursing, clinical governance, education and nursing professional development, she has built an in-depth understanding of the educational and regulatory needs of the Australian healthcare sector.
As the Accredited Provider Program Director (AP-PD) of the Ausmed Education Learning Centre, she maintains and applies accreditation frameworks in software and education. In 2024, Zoe lead the Ausmed Education Learning Centre to achieve Accreditation with Distinction for the fourth consecutive cycle with the American Nurses Credentialing Center’s (ANCC) Commission on Accreditation. The AELC is the only Australian provider of nursing continuing professional development to receive this prestigious recognition.
Zoe holds a Master's in Nursing Management and Leadership, and her professional interests focus on evaluating the translation of continuing professional development into practice to improve learner and healthcare consumer outcomes. From 2019-2022, Zoe provided an international perspective to the workgroup established to publish the fourth edition of Nursing Professional Development Scope & Standards of Practice. Zoe was invited to be a peer reviewer for the 6th edition of the Core Curriculum for Nursing Professional Development.



