Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders, affecting about 0.6% of Australians (AIHW 2022).
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition that causes an individual to experience recurrent seizures (WHO 2023).
It’s important to note that the term epilepsy refers to a range of disorders that can cause seizures; it is not a singular condition. For this reason, people with epilepsy have varying experiences (Healthdirect 2022; Epilepsy Action Australia 2023).
While epilepsy can affect anyone, people are more likely to be diagnosed in childhood or older age (Epilepsy Action Australia 2023).
Epilepsy may eventually stop with age or be a life-long condition, but the seizures it causes can often be controlled using medication (Epilepsy Action Australia 2023).
Epilepsy v Seizures
These two terms are related but not interchangeable.
A seizure is a sudden neurological event in which the electrical impulses in the brain are disrupted by an uncontrolled surge of electrical activity (Epilepsy Action Australia 2023; Better Health Channel 2023a).
This may result in symptoms such as:
- Loss of consciousness
- Loss of awareness or blank staring
- Convulsions and involuntary movements
- Confusion or disorientation
- Falling
- Sensory disturbances
- Automatisms
- Sleep disturbances
- Incontinence
- Headache
- Pain
- Tiredness.
(Epilepsy Action Australia 2023; Epilepsy Foundation 2019a; Healthdirect 2021)
Seizures vary in severity and usually last for up to two to three minutes (Epilepsy Action Australia 2023).
While epilepsy causes an individual to experience seizures, having a seizure does not necessarily mean an individual has epilepsy. Epilepsy is generally diagnosed if someone has had at least two unprovoked seizures, but about half of the people who have one seizure will never experience another one (Healthdirect 2022; WHO 2023).
Causes of Epilepsy
Only about half of people with epilepsy are able to have the cause of their condition identified (Epilepsy Action Australia 2023). Potential causes include:
- Head injury (e.g. due to trauma, an accident or a fall)
- Stroke or brain haemorrhage
- Lack of oxygen to the brain for a long period of time (e.g. birth trauma, cardiac arrest, drowning, drug overdose)
- Brain infection (e.g. meningitis, encephalitis or brain abscess
- Brain abnormalities at birth
- Brain tumours
- Genetics
- Degenerative conditions that affect the brain (e.g. dementia)
- Heavy alcohol or drug use.
(Epilepsy Action Australia 2023; Healthdirect 2022)
Types of Seizures
Read: Seizure Types and Nursing Management
Seizure Triggers

The following factors (depending on the individual) may trigger people with epilepsy to have a seizure:
- Insufficient sleep
- Insufficient hydration
- Low blood glucose
- Emotional and physical stress
- Missing or changing medicines
- Alcohol
- Certain recreational and prescription drugs
- Flickering lights or patterns
- Stress
- Menstruation
- Illness, especially if the individual is experiencing diarrhoea or vomiting
- Significant changes to body temperature.
(Better Health Channel 2023a; Epilepsy Foundation 2019a)
The Impact of Epilepsy on the Individual
Epilepsy may significantly affect an individual’s quality of life (Vaurio et al. 2016).
People who are newly diagnosed with epilepsy may have difficulty adjusting, particularly if they need to take new medicines or make changes to their lifestyle (Epilepsy Action Australia 2022a).
Mental illness is prevalent among people with epilepsy, with about 50% experiencing depression (two to three times more than the general population) and 20% experiencing anxiety (Epilepsy Foundation 2019b; Epilepsy Action Australia 2022b).
While about 70% of people with epilepsy are able to control their seizures with medication, those who still experience seizures or have untreated or poorly-controlled epilepsy are at risk of injury, falls and even death, especially if seizures occur without notice (Better Health Channel 2023b).
People with epilepsy are also up to three times more likely to suffer premature mortality (WHO 2023).
Epilepsy may have a variety of other impacts, including:
- Loss of functional capacity and independence (e.g. not being able to drive)
- Disability
- Seizure-related injuries (e.g. bruises, fractures)
- Stigmatisation
- Reduced social support
- Lack of participation in activities due to fear of seizures
- Impaired ability to work, potentially leading to lower-income or unemployment
- Overall decrease in quality of life.
(AJMC 2020; Vaurio et al. Barr 2016; WHO 2023; Epilepsy Action Australia 2022a)
Treatment Options for Epilepsy
While epilepsy has no cure, there are treatment options. Depending on the individual, these may include:
- Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) to control seizures
- Emergency medication if the client has frequent or long seizures
- Diet (Ketogenic diet or modified Atkins diet
- Surgery to remove an area of epilepsy focus (abnormal brain tissue).
(Epilepsy Foundation 2019a)
Nursing Management and First Aid for Seizures
Read: Seizure Types and Nursing Management
Practical Tips for Caring for Clients With Epilepsy
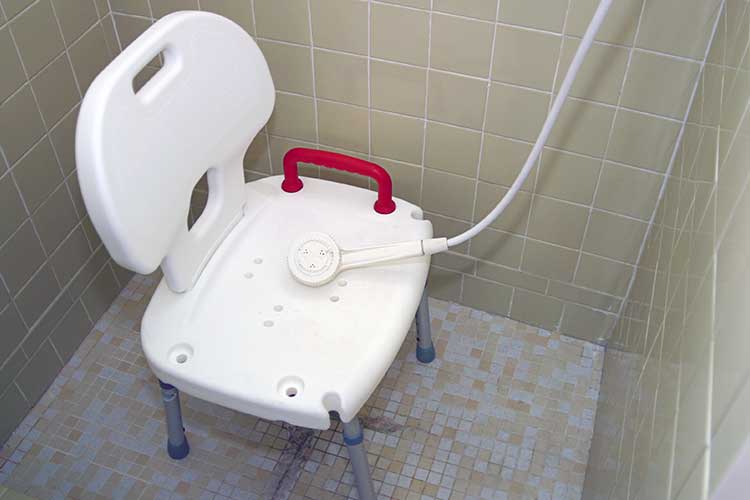

The following are some tips for caring for clients who have epilepsy, especially in aged care settings:
- If the client is taking AEDs, these may interact with other medicines and treatments. Always assess the potential for interaction before administering a medicine or treatment.
- If a client who takes AEDs is required to fast for a particular procedure, the first step is to liaise with medical staff and ensure they are aware that the client requires AEDs. You should discuss whether it is appropriate to withhold the AEDs during the fasting period.
- If a client is experiencing seizures, document the duration of symptoms, the frequency of the seizures and the ways in which the seizures are affecting the client. Consider filming the seizure as a video record (only with the client’s consent). Consider having a discussion upon the client's admission or at an appropriate time to establish consent for filming if a seizure was to occur.
- Ensure clients are getting adequate sleep, nutrition, exercise and stimulation.
- Consider devices and assistive technologies (e.g. medical bracelets, ID cards, fall detector pendants) that will help ensure the client’s safety.
- Bathe clients in the shower rather than the bath, as this is safer. Use a shower chair if possible.
- Consider softer floor surfaces such as soft wool carpeting or cushioned linoleum, as these are safer in the event of a fall.
- Remove clutter and tripping hazards.
- Provide clients with firm pillows rather than soft pillows, as these are less likely to cause suffocation in the event of a seizure.
- Ensure you are appropriately trained in seizure first aid and know how to keep the client safe during a seizure.
- Support any required interventions (e.g. psychotherapy, support groups) and refer the client if necessary.
(Epilepsy Foundation 2019a, c)
Conclusion
While epilepsy can often be managed, seizures have the potential to result in serious harm. Therefore, understanding this condition and knowing how to keep a client safe in the event of a seizure is essential.
Test Your Knowledge
Question 1 of 3
What percentage of people with epilepsy are able to control their seizures with a medicine?
Topics
References
- American Journal of Managed Care 2020, ‘Examining the Economic Impact and Implications of Epilepsy’, AJMC, viewed 27 September 2023, https://www.ajmc.com/view/examining-the-economic-impact-and-implications-of-epilepsy
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2022, Epilepsy in Australia, Australian Government, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/chronic-disease/epilepsy-in-australia/contents/summary
- Better Health Channel 2023a, Epilepsy, Victoria State Government, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/epilepsy
- Better Health Channel 2023b, Epilepsy - First Aid and Safety, Victoria State Government, viewed 27 September 2023, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/ConditionsAndTreatments/epilepsy-first-aid-and-safety
- Epilepsy Action Australia 2022b, Epilepsy and Depression, Epilepsy Action Australia, viewed 27 September 2023, https://www.epilepsy.org.au/e-quip-an-epilepsy-resource-for-youth/epilepsy-and-depression/
- Epilepsy Action Australia 2022a, Living with Epilepsy, Epilepsy Action Australia, viewed 27 September 2023, https://www.epilepsy.org.au/about-epilepsy/living-with-epilepsy/
- Epilepsy Action Australia 2023, Understanding Epilepsy, Epilepsy Action Australia, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.epilepsy.org.au/about-epilepsy/understanding-epilepsy/
- Epilepsy Foundation 2019c, AED Side-Effects and Interactions, Epilepsy Foundation, viewed 27 September 2023, https://epilepsyfoundation.org.au/understanding-epilepsy/treatments-and-management/anti-seizure-medication/asm-side-effects-and-interactions/
- Epilepsy Foundation 2019a, Epilepsy in the Later Years: An Epilepsy Smart Aged Care Approach, Epilepsy Foundation, viewed 26 September 2023, https://epilepsyfoundation.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/1532-UM_SM-Inclusive-Aged-Care-PracticesFINAL.pdf
- Epilepsy Foundation 2019b, Mental Health, Epilepsy Foundation, viewed 27 September 2023, https://epilepsyfoundation.org.au/managing-epilepsy/health-and-wellbeing/mental-health/
- Healthdirect 2022, Epilepsy, Australian Government, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/epilepsy
- Healthdirect 2021, Seizures, Australian Government, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/seizures
- Vaurio, L, Karantzoulis, S & Barr, W B 2016, ‘The Impact of Epilepsy on Quality of Life’, in Chiaravalloti, N D & Goverover Y (ed.), Changes in the Brain, Springer, New York, NY, viewed 27 September 2023, https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-0-387-98188-8_8
- World Health Organisation 2023, Epilepsy, WHO, viewed 26 September 2023, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
 New
New